Environment Management Division (EMD)
Founded on 23rd June 1988, EMD stands as a cornerstone of Steel Authority of India Limited (SAIL), operating from its corporate headquarters in Kolkata. With a clear mandate, EMD leads the charge in sustainable environmental stewardship, driving strategic initiatives and ensuring robust environmental governance across all SAIL plants, units, and mines. Its mission: to embed eco-conscious practices into the company’s core operations and foster a culture of sustainability enterprise-wide.
Purpose & Role
EMD serves as SAIL’s strategic advisor and coordinator for environmental and pollution control efforts across all facilities. It drives company-wide initiatives in sustainability, resource optimization, and environmental awareness.
Core Responsibilities
- Performance Review: Evaluates environmental performance of plants, units, and mines.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensures adherence to environmental laws and facilitates company-wide compliance.
- MIS Development: Builds systems to monitor and manage environmental data.
- Governance Reporting: Updates SAIL’s Board on compliance via the Health, Safety & Environment Sub-committee.
- Sustainability & ESG:
- Prepares sustainability reports and manages ESG risks.
- Enhances ESG ratings and supports Sustainable Development projects.
- Develops environmental policies and strategic frameworks.
Support Functions
- Clearances: Assists in obtaining EC, CtE, CtO, and Auithorisations.
- Optimization: Manages waste, conserves water, promotes plantations, and supports climate initiatives like LCA and decarbonization.
- Standards: Implements EMS and ISO 14001 certification.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Coordinates with government bodies and industry associations (WSA, ISA).
Strategic & Capacity Initiatives
- Reviews environmental aspects of project proposals.
- Manages data for parliamentary queries.
- Facilitates participation in environmental awards.
- Conducts workshops and training to build environmental competencies across SAIL.
SAIL’s Commitment to Eco-System Protection: A Decade of Green Progress
SAIL champions environmental sustainability through its robust Corporate Environment Policy and visionary leadership. With the EMD at its helm, the company goes beyond mere compliance—embedding eco-friendly practices across its plants, units, mines, and neighboring communities. EMD drives strategic initiatives that not only meet but often surpass regulatory standards, reinforcing SAIL’s commitment to responsible growth and environmental stewardship.
Environmental Performance: A Decade of Transformation
SAIL’s focused environmental initiatives have led to remarkable improvements between 2015-16 and 2024-25:
|
Sl. No. |
Parameter |
Unit |
2024-25 |
2015-16 |
Improvement (%) |
|
1 |
Specific PM Emission Load |
kg/tcs |
0.56 |
0.81 |
31 |
|
2 |
Specific CO2 Emission |
T/tcs |
2.55 |
2.60 |
2 |
|
3 |
Specific Water Consumption |
m³/tcs |
3.00 |
3.83 |
22 |
|
4 |
Specific Effluent Discharge |
m³/tss |
1.26 |
2.14 |
41 |
|
5 |
Specific Effluent Load |
kg/tcs |
0.05 |
0.09 |
43 |
|
6 |
BF Slag Utilisation |
% |
99 |
89 |
11 |
|
7 |
BOF Slag Utilisation |
% |
137 |
78 |
76 |
|
8 |
Total Solid Waste Utilisation |
% |
107 |
84 |
27 |
Note: Values exceeding 100% indicate utilization of stock from previous years.
Key Highlights
- Emission Control: 31% reduction in PM emissions and 2% drop in CO₂ emissions reflect cleaner air initiatives.
- Water Efficiency: 22% decrease in water consumption signals smarter resource use.
- Waste Utilization: BOF slag utilization surged by 76%, with total solid waste reuse up by 27%.
- Effluent Management: Effluent discharge and load reduced by over 40%, improving water quality and ecosystem health.
Toward a Greener Tomorrow: SAIL’s Sustainability Journey
Over the last ten years, SAIL has consistently championed environmental stewardship. Guided by its EMD, the company has become a trailblazer in sustainable steel production—showing that robust industrial growth can go hand in hand with responsible ecological practices.
Climate Change Mitigation
SAIL acknowledges the urgency of climate change, primarily driven by industrial emissions. As a major contributor, the steel sector is embracing decarbonization through:
- CO₂ emission reduction
- Carbon capture technologies
India’s Climate Goals & SAIL’s Role
India ratified the Paris Agreement in 2016, pledging net-zero emissions by 2070. In alignment:
- SAIL targets CO₂ emission intensity 2.19 T/tcs by 2030
- Supports national climate commitments through strategic action
SAIL’s Climate Action Vision
SAIL’s Corporate Environment Policy promotes:
- Reduction in greenhouse gas emissions
- Expansion of green cover
- Adoption of energy-efficient technologies
- Increased use of renewable energy
Path to Carbon Neutrality
Clean Technology Adoption
- Coke Oven Batteries with Coke Dry Cooling Plants
- Blast Furnace upgrades: TRT, CDI, WHR
- WHR systems in Sinter Plants
- Energy-efficient reheating furnaces
- VVVF drives, IE3 motors, and gas-fired boilers
Renewable Energy Expansion
- Solar systems in hospitals, guest houses, and facilities
- 17.595 MW solar + 7 MW bagasse-based energy commissioned
- Goal: 384 MW renewable capacity by 2028–29
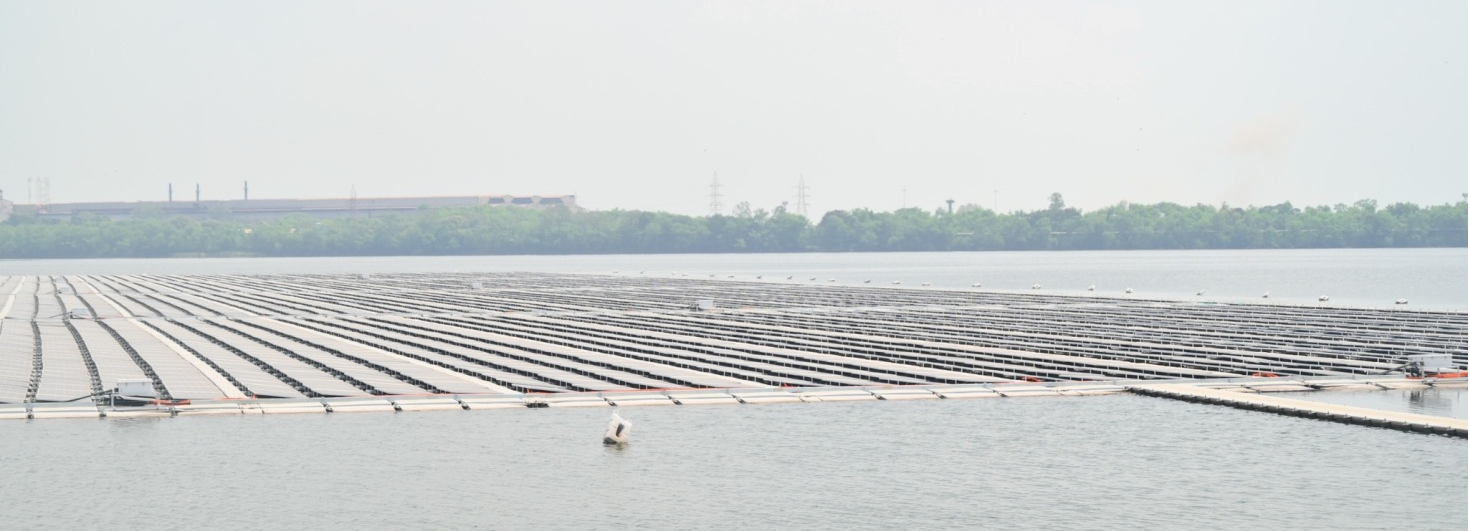

Photo: 5 MW floating Solar Power Plant at the Maroda-1 reservoir of BSP
LED Transition
- Installed 1.3 million+ LED lights under UJALA Scheme
- Continued upgrades to energy-efficient lighting systems
Decarbonization Strategy
|
Timeframe |
Focus Areas |
|
Short Term (by 2030) |
Efficiency improvements & renewable energy |
|
Medium Term (2030–2047) |
Green Hydrogen & CCUS integration |
|
Long Term (2047–2070) |
Disruptive technologies for net-zero |
Collaborative Path to Carbon Neutrality
Decarbonisation Partnerships
- SMS Group & BSP: Green steelmaking, Coke Oven Gas Injection
- Primetals & RSP: Hydrogen steel, CCUS, digitalization
- RDCIS & BHP: BF-BOF decarbonisation pathways
- RDCIS & IOCL: Moisture-reducing fluid for coke
- GIZ–SCOPE: Feasibility study on scrap, tailings, hydrogen
- LeadIT Initiative: Projects in Hydrogen DRI, CCUS, BF excellence, dry beneficiation, biomass
Biomass Utilization
- Biochar Trials: Bamboo biochar in sinter production (DSP)
- Blast Furnace Co-Injection: Biochar with pulverized coal to reduce emissions and improve efficiency
CCUS Projects
- RCPL Partnership: CO₂ capture and conversion into ethanol, methanol, acetates
- Tripartite Agreement: ISP, IIT Bombay, GEECL exploring CCUS in CBM wells
Hydrogen Integration
- Blast Furnace Pilot: ₹50 crore project under National Green Hydrogen Mission
- DRI Collaboration with IIT Kharagpur: Lab and pilot setups to optimize hydrogen-based DRI production
SAIL’s multi-pronged strategy—spanning clean tech, renewables, biomass, CCUS, and hydrogen—demonstrates its leadership in sustainable steelmaking and unwavering commitment to India’s climate goals.
Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs) - A Strategic Edge for Sustainability
In today’s sustainability-focused market, Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs) offer manufacturers a competitive edge by providing transparent, third-party-verified data on a product’s environmental impact across its life cycle—aligned with ISO 14025 standards.
As governments and institutions increasingly mandate EPDs for climate action and green procurement, EMD has initiated the development of EPDs for steel products across its plants. This move reinforces SAIL’s commitment to sustainability, transparency, and global best practices in low-carbon manufacturing.
Water Conservation at SAIL: A Sustainable Commitment
EMD drives policy, monitors performance, and ensures compliance—making water conservation a strategic priority across SAIL. Its efforts reflect a holistic approach to balancing industrial growth with environmental responsibility.
SAIL recognizes water as a vital resource and has embedded conservation into its operations across plants, units, and mines. With strategic leadership from the Environment Management Division (EMD), the company has implemented several high-impact initiatives to promote sustainable water use.
Key Initiatives
Effluent & Sewage Treatment: Effluent Treatment Plants (ETPs) and Sewage Treatment Plants (STPs) treat and recycle industrial and domestic wastewater, meeting environmental standards.
Coke Dry Cooling Plants (CDCP): Replaces water-based coke quenching and Conserves water, prevents contamination, and generates power via heat recovery.
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD): Salem Steel Plant and Chandrapur Ferro Alloy Plant operate on ZLD principles. ~128 million m³/year of wastewater is already recycled at SAIL plants. All new projects follow ZLD design.

Photo: ZLD scheme for Outfall#1, 2, & 3 at DSP
Water Use Efficiency: Achieved a 22% reduction in specific water consumption (from 3.83 to 3.00 m³/tcs between 2015–2025).
Rainwater Harvesting (RWH): Site-specific systems recharge groundwater. Integrated with the “Catch the Rain” campaign and future project specs.
Waste Management: A Commitment to Sustainability
As part of its Corporate Environmental Policy, SAIL is committed to minimizing solid waste generation and maximizing its reuse striving for 100% utilization through the principles of Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, Recover (4Rs). EMD plays a pivotal role in steering these efforts across all operations.
Industrial Waste Management Initiatives
Blast Furnace (BF) Slag: All BFs are equipped with slag granulation plants, enabling 100% reuse in cement production.
Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF) Slag: Metallics are recovered and recycled into sinter-making or flux replacement. BOF slag is also supplied to external agencies for construction applications.
Other Process Wastes: By-products like flue dust, mill scale, lime/dolo fines, and refractory waste are reused internally or sold for further processing.
Waste-to-Wealth Innovations
R&D Collaborations: Joint studies with leading institutions to enhance BOF slag utilization.
BOF Slag Applications: Used for internal roads and rural infrastructure under PMGSY. Converted into paver blocks, green tiles, and explored for brick-making and runner sand substitution.
Agricultural Use of BOF Slag: In partnership with ICAR-IARI, SAIL supports the development of eco-friendly fertilizers using lime-rich BOF slag. 13 Steel Slag-Based Value-Added Products (SSBVAPs) have been developed—10 for general agriculture and 3 tailored for acidic soils.




Photo: Independent Field Trials at ISPs
MoU with RCPL: Circular Economy in Action
Bokaro Steel Plant has signed an MoU with M/s RCPL to recover Silicon (Si) and Silicon Carbide (SiC) from BOF slag, advancing SAIL’s circular economy goals through resource recovery and waste valorization.
Hazardous & Biomedical Waste
Hazardous Waste: Includes spent oil, sludge, and industrial residues—safely disposed via secured landfills or authorized agencies.
Biomedical Waste: Managed as per regulatory norms across SAIL’s hospitals and health centers.
Domestic Waste Management: Door-to-door collection & segregation and vat-based systems ensure organized waste handling. Solid Liquid Resource Management (SLRM) Centre at Bhilai Steel Plant processes domestic waste into manure and plastic by-products. Bio-Digesters: Installed at DSP, RSP, and BSL to convert canteen waste into compost for horticulture.
Plastic Waste: Segregated and sent to registered recyclers. Awareness & Training: Campaigns and workshops promote hygienic practices and discourage single-use plastics.
Sustainable Plastic Disposal:
BSP initiated a step to recycle waste plastics in its Coke Oven Batteries. Waste plastic granules mixed with coal-blend for energy recovery and improved coking.
RSP executed 1 km pilot road built using plastic-bitumen mix, showcasing sustainable infrastructure potential.
Greenery & Biodiversity at SAIL
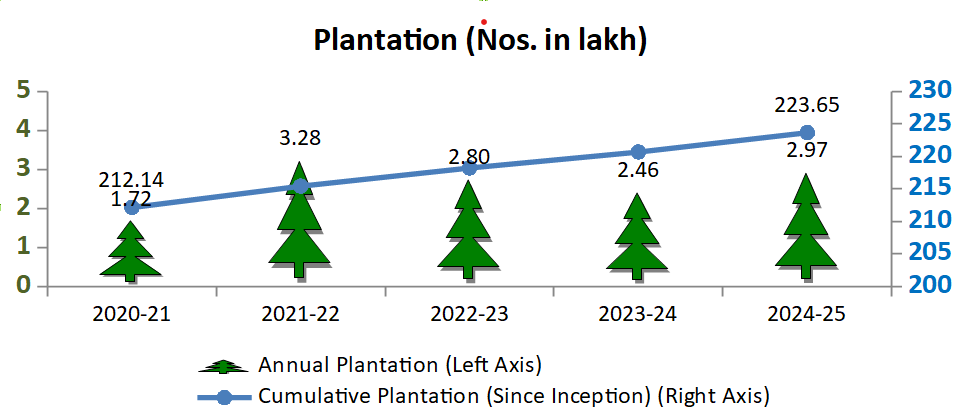
EMD drives structured plantation programs across plants, units, and mines. In 2024–25, 3 lakh saplings were planted, adding to a cumulative 22.4 million, enhancing green cover and supporting climate action.
Biodiversity Conservation
EMD facilitates structured greenery development across SAIL’s plants, units, and mines by guiding plantation programs, promoting native species, and ensuring ecological alignment with local soil and climate conditions. The VASUNDHARA Biodiversity Park at DSP spans 409 acres, offering ecological balance and a serene retreat for nearby communities.
Eco-Restoration of Mined Out Lands
SAIL has restored 450 acres of degraded land at Purnapani Mines with Delhi University, creating a thriving ecosystem. In partnership with IFP Ranchi, new projects at MIOM and KIOM, aim to rehabilitate 18.5 hectares by 2025–26 and at GOM to rehabilitate 16 hectares by 2029-30 have been taken — reinforcing sustainable mining and environmental stewardship.
EMS Implementation at SAIL
SAIL, with guidance from EMD, has been a pioneer in adopting the Environment Management System (EMS) aligned with ISO 14001 standards. Starting at Salem Steel Plant in the mid-1990s, EMS has since been implemented across all integrated plants, major units, and warehouses. This system helps manage environmental impacts and ensures operations not only meet but often exceed regulatory norms—reinforcing SAIL’s commitment to sustainable industrial practices and environmental stewardship.
Green Certifications at SAIL
GreenPro Ecolabel by CII helps identify eco-friendly products and technologies in manufacturing and construction. Accredited by the Global Ecolabelling Network (GEN), it ensures global environmental standards.
DSP became the first PSU steel plant in India to earn GreenPro certification for its TMT Rebars and Structural Steel, showcasing its commitment to sustainable steelmaking.
GreenCo Rating, also by CII, evaluates a company’s environmental performance and supports its journey toward net-zero emissions. BSL has signed an Expression of Interest (EOI) to participate, reinforcing its dedication to green manufacturing excellence.
Environmental Awards & Recognition
EMD plays a central role in driving SAIL’s environmental excellence. It coordinates sustainability initiatives, monitors performance, and compiles data to support award nominations. By aligning operational practices with national and global environmental standards, EMD ensures that SAIL’s plants and mines consistently earn accolades reinforcing the company’s leadership in responsible industrial practices.
In 2024–25, several plants and units were recognized for outstanding environmental performance.
- SAIL adjudged as “Circularity Champion” in the “Outlook Planet Sustainability Summit & Awards 2024” by the Outlook Group.

- SAIL declared as WINNER of the “Golden Peacock Environment Management Award 2024” in Steel Sector category by the Institute of Directors.

- SAIL as a whole and BSL conferred with 5 Star Rating in the “Kalinga Environment Excellence Award 2023” organised by the Institute of Quality and Environment Management Services (IQEMS), Bhubaneswar in association with Odisha State Pollution Control Board.

- EMD and RSP adjudged as the WINNER of “Greentech PCWR Award 2024” in ‘PCWR Excellence Category’ by Greentech Foundation.
- BSP adjudged as the WINNER of “Greentech PCWR Award 2024”in ‘Innovative Waste Management Technology Category’ by Greentech Foundation.

- RSP bagged the prestigious “GEEF Global Sustainability Award 2024” instituted by the Global Energy & Environment Foundation (GEEF).

